6 February 2018 marked 100 years since the Representation of the People Act 1918 – the act which allowed some women in the UK the right to vote. This was a major landmark in the history of our democracy.
Influential consideration
Only 58% of the adult male population was eligible to vote before 1918. An influential consideration, in addition to the suffrage movement and the growth of the Labour Party, was the fact that only men who had been resident in the country for 12 months prior to a general election were entitled to vote.
This effectively disenfranchised a large number of troops who had been serving overseas in the war. With a general election imminent, politicians were persuaded to extend the vote to all men and some women at long last.
Representation of the People Act 1918

In 1918 the Representation of the People Act was passed which allowed women over the age of 30 who met a property qualification to vote. Although 8.5 million women met this criteria, it only represented 40 per cent of the total population of women in the UK.
The same act abolished property and other restrictions for men and extended the vote to all men over the age of 21. Additionally, men in the armed forces could vote from the age of 19. The electorate increased from eight to 21 million, but there was still huge inequality between women and men.
Why women needed the vote
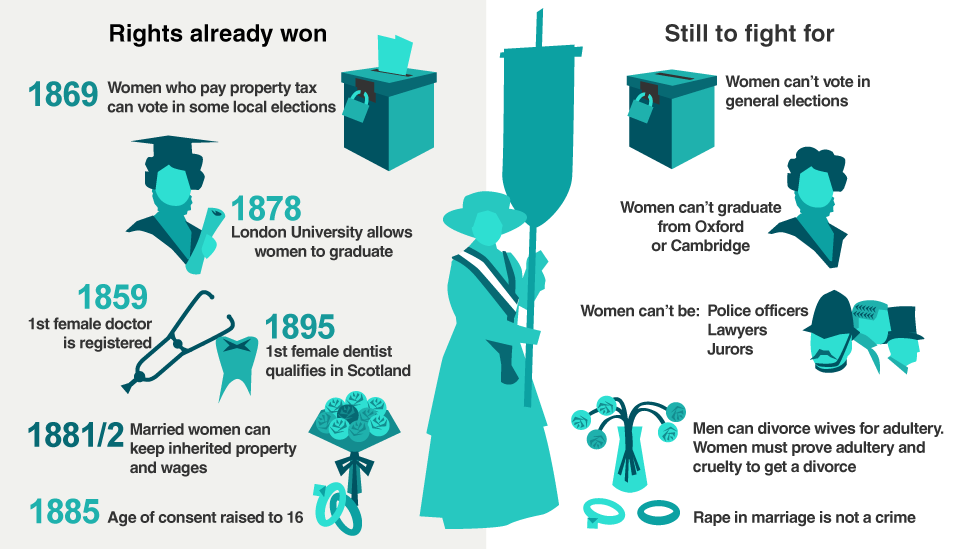
Women had argued for – and won – new rights in the 19th Century. However, without the vote campaigners thought there was little incentive for politicians to improve the lives of women further. They believed MPs only cared about issues that affected the men who were able to vote for them.
Equal Franchise Act 1928
It was not until the Equal Franchise Act of 1928 that women over 21 were able to vote and women finally achieved the same voting rights as men. This act increased the number of women eligible to vote to 15 million.






Leave a Reply